New biocompatible products shagaol and curcuminoid-like type used as adjuvantes in cancer radiotherapy
CANRADIOPROTECT
Home
Contracting authority: Executive Unit for the Financing of Higher Education, Research, Development and Innovation – UEFISCDI
Project number: PN-III-P2-2.1-PED-2019-1471
Partners: National Institute for Research & Development in Chemistry and Petrochemistry –ICECHIM
University of Bucharest, The Faculty of Biology
Contract number: 363PED/2020
Implementation period: 2020-2022
Budget: 600.000 lei
About
The proposal has as a general objective the obtaining of keto-enolic derivatives of natural origin and of synthesis. This project refers to an interdisciplinary field of research and aims to elaborate methods of synthesis and biological testing of new compounds, symmetrical β-di-ketones (curcumin derivatives) and asymmetric mono or di-ketones (shagaol derivatives). After morphostructural characterization, biocompatibility testing and establishing the structure-property relationship, biologically active products will be applied in the radiotherapy treatment of cancer. In this way it is expected that the new structures synthesized, analogues of shagaol and curcumin, have higher antitumor activity than that of natural compounds and be used as adjuvants in cancer therapy.
Obiectives
O1. Selection of natural compounds and synthesis of biologically active chromogens (curcumin and shagaol) with free radical capture properties and
choice of demonstrative experimental model.
O2. The study of the radioprotective and radio sensitizing processes of the compounds selected after the biocompatibility tests.
O3. The correlation of the intensity of the effect of radioprotection and radiosensitization with the structural characteristics of the selected compounds.
Estimated results:
New products:
• 2 compounds derived from curcumin with radioprotective / radiosensitizing properties;
• 2 analogous shogaol compounds with radioprotective / radiosensitizing properties.
Obtaining technologies and methods of application:
Technology for obtaining keto-ethylene products with radioprotective / radiosensitizing properties.
Method and conditions of treatment for radiotherapy and radiation protection of whole erythrocyte.
The main results regarding the synthesis, characterization and radioprotective or radiosensitizing properties manifested by new keto-enol derivatives will be disseminated by nationally and internationally publication in specialized scientific journals: 5 articles ISI, 6 scientific communications at international conference and 2 national patent applications.
Project development
Stage 1 – 2020
Selection of natural compounds with antioxidant properties and elaboration of concept design of the experimental model.
Following the analysis of data published in the literature on active compounds extracted from turmeric, the team from INCD-ICECHIM (CO) starts the
first experimental activities aimed at the extraction by classical methods of maceration and decoction of curcumin derivatives from turmeric root.
The aqueous extracts obtained were analyzed by thin layer chromatography and UV-Vis spectroscopy, and the solid residue from the extraction process was analyzed by FTIR spectroscopy, reflectance spectroscopy and thermogravimetric analysis. These studies were performed in order to identify, isolate and characterize the main compounds found in natural extracts of Curcuma Longa (turmeric).
In parallel, the research team of the partner, University of Bucharest (UB), conducted testing studies on two different cell types, the HeLa tumor cervix cell line, compared to the MRC-5 non-tumor cell line, to be able to highlight a specificity of action on malignant cells.
An Isolera Prime flash chromatograph system was purchased at this stage of the project. This makes it possible to separate the compounds from the mixtures or to characterize the unitary compounds in terms of purity. The device is useful in the project for conducting studies to evaluate plant mixtures obtained under different extraction conditions and for the characterization of newly synthesized compounds in the process of their separation and purification.
Isolera Prime is a high performance flash chromatography system consisting of the following integrated components:
• A solvent-resistant, color LCD touch screen with a resolution of 800 x 600 pixels. It serves both as a display and as a system input device via the touch controls on the screen.
• A fraction collector.
• A pump module, which directs the flow of liquid through the system.
• An internal detector, which provides the system with information on the light absorbance of solvents and samples passing through the flow cell of the detector.
Stage 2 – 2021
Alternatives for obtaining natural or synthetic compounds, choosing the functional model and testing them in the processes involved in radiotherapy
In the second stage, studies on the methods of extraction and characterization of the main compounds from turmeric and ginger were continued by CO, using the soxhlet method, microwave field extraction and assisted extraction by ultrasonic processes, in water or alcohol. The natural extracts obtained were characterized for the identification of the main constituent compounds, by thin layer chromatography, and then the compounds were separated by the ˮflash chromatographyˮ process. The separated fractions were analyzed by UV-Vis spectroscopy, and together with the residual mass resulting from the extraction processes were characterized by FTIR spectra and diffuse reflection spectra.
Similar to the structures of the natural compounds curcumin and shagaol, extracted from turmeric and ginger, respectively, a series of compounds were synthesized using the solvent method or the microwave field. Thus, bis-aryl-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dionic chromogens obtained in the microwave field. While curcuminic derivatives, 3,5-bis (styryl) pyrazolonic compounds were synthesized by the classical method. In parallel, 6-aryl-5-hexene-2,4-dione derivatives were synthesized by solvent-free in the microwave field. The compounds resulted from the condensation reaction between substituted benzaldehydes with acetylacetone, hexanal. At the same time, 6-aryl-5-hexen-2-one structures were obtained by the conventional solvent method, following successive condensation reactions between substituted benzaldehydes with acetone and then with hexanal. The synthesized compounds were purified by specific methods and characterized by thin layer chromatography, FTIR spectroscopy, UV-Vis spectroscopy, NMR and thermogravimetric analysis.
The UB partner, following the concept design established in the first stage, tested the curcumin and shagaol derivatives, synthesized by CO, using
the two in vitro cellular models, for the biocompatibility and toxicity tests, respectively. In parallel, in order to establish the treatment technology, the
efficiency of blood cells as cell models for the evaluation of the properties exerted by curcumin derivatives was first tested. The method chosen to
determine the activity of the enzyme glutathione peroxidase GPx is based on monitoring the formation of GSSG (glutathione disulfide), which is continuously reduced by adding an excess of glutathione reductase, generating a constant level of GSH (Glutathione). After choosing the test method, from the batch of compounds analyzed in terms of biocompatibility and cytotoxicity, two compounds were selected that showed very low cytotoxicity. These beta-diketone derivatives with the styryl-pyrazolonic structure and the curcumin standard were subjected to tests performed by exposure to gamma radiation (10 or 50 Gy), regarding the evaluation of the radiation protection properties on erythrocytes. Samples of erythrocyte membranes resulting from erythrocyte lysis and removal of intracellular contents were analyzed by THz spectroscopy. The test results showed that in terms of radiation protection, 3,5-bis (styryl) pyrazolone appears to be the most effective.
In order to test the radioprotection efficiency of shogaol derivatives on erythrocytes, biochemical analyzes were performed. After irradiation with gamma radiation dose of 50 Gy, the GPx activity of treated erythrocytes remains at the same level as that of treated and non-irradiated erythrocytes, showing that shogaol derivatives prevented an additional decrease in GPx activity due to irradiation. Thus, a radioprotective effect of shogaol derivatives (Sh1 and Sh3) is highlighted.
Stage 3 – 2022
The correlation of the intensity of the effect of radioprotection and radiosensitization with the structural characteristics of the selected compounds
After confirming the radioprotective/radiosensitizing properties of the four compounds derived from curcumin (P2, P7) and shogaol (Sh1, Sh3), optimal synthesis parameters were established to obtain the active compounds.
The technology for obtaining 3,5-bis(styryl)pyrazolonic curcumin derivatives was presented by establishing the laboratory equipment and raw materials used in the synthesis process, the technological stages and the way of working with the sequence of phases and operations that will be carried out.
In order to develop the demonstrative experimental model, the phagocytic activity of human blood granulocytes was investigated using flow cytometry by evaluating the oxidative burst after their stimulation with Escherichia coli. The obtained results showed that, although the irradiation of the control caused a decrease in the number of positive granulocytes, the pre-incubation with curcumin derivatives restored the level to that of the control. In the case of shogaol derivatives, there were no significant differences compared to the non-irradiated or irradiated control. In the case of shogaol derivatives, there were no significant differences compared to the non-irradiated or irradiated control. To establish the treatment conditions, bioinformatics methods were used to predict the relationship between the structure and the biological effect of the four radioprotective/radiosensitizing derivatives.
First of all, the similarities between the derivatives and the drug molecules were checked from the point of view of the physico-chemical properties. P2, Sh1 and Sh7 are in the optimal ranges specific to drug molecules, while the properties of P7 deviate from these ranges. Compounds P2, Sh1 and Sh3 appear as bioavailable for oral administration, suggesting that they are able to circulate to the place where they will exert their biological effect. P7 is not bioavailable, which suggests that in its case it will be necessary to increase bioavailability possibly by using some targeted delivery mechanisms. According to predictions, the compounds are adsorbed in a very high proportion in the small intestine or through the skin.
Taking these recommendations into account, the compounds obtained and validated as having radioprotective/radiosensitizing properties were conditioned in the form of creams or hybrid materials for targeted delivery and can be used as adjuvants in radiotherapy.

Figure 1: Compound P2 (2-phenyl-3,5-bis(styryl)pyrazole derivative) conditioned as w/o emulsion.

Figure 2: Nanocomposite G718 (ginger extract-SeNP) conditioned as o/w emulsion.
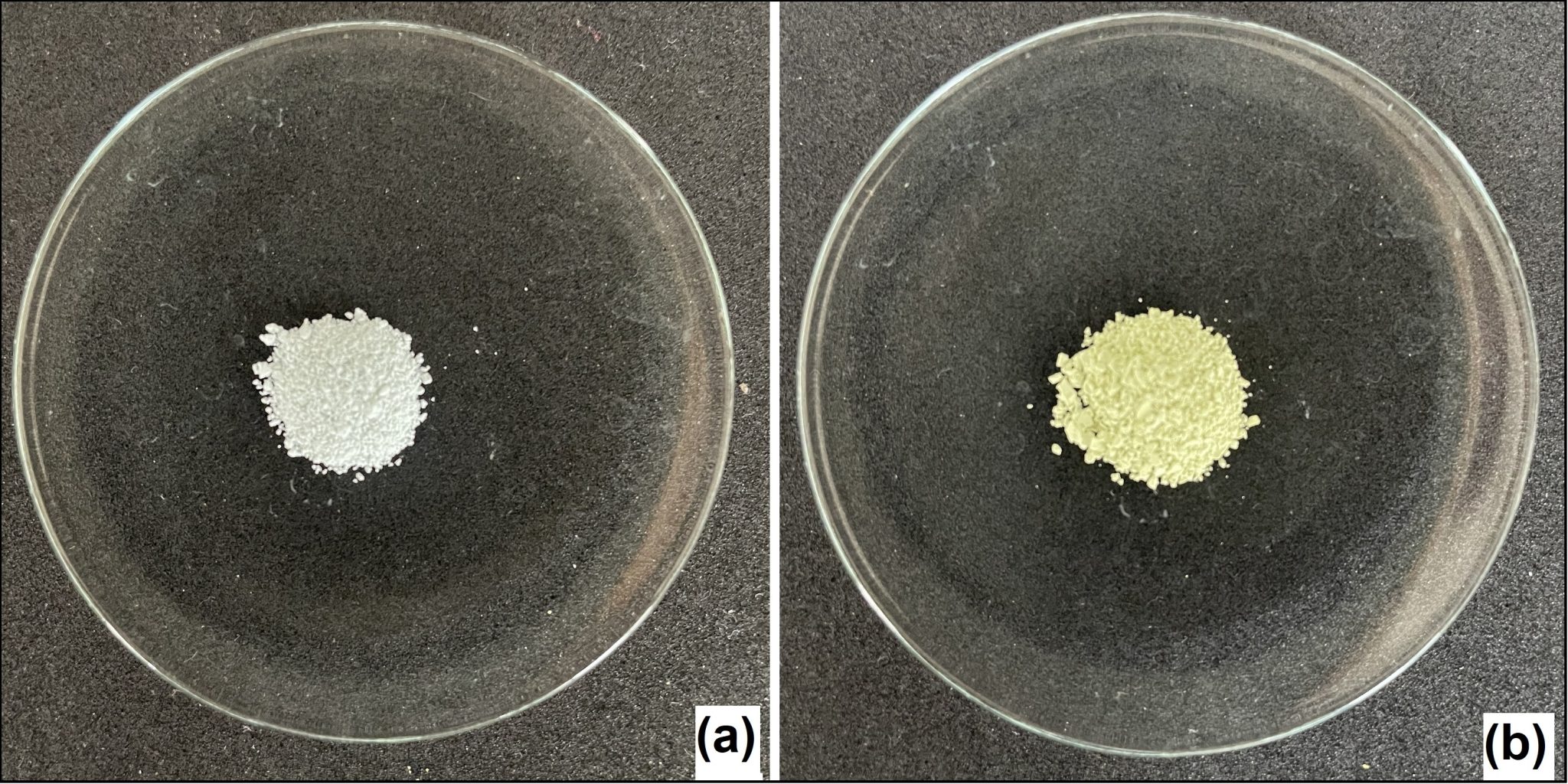
Figure 3: Hybrid materials – shogaol derivatives Sh1 (a) and Sh3 (b) loaded on palygorskite.
Results
Papers
1. Raduly, F.M.; Raditoiu, V.; Raditoiu, A.; Frone, A.N.; Nicolae, C. A.; Purcar, V.; Ispas, G.; Constantin, M.; Raut, I. “Modeling the properties of curcumin derivatives in relation to the architecture of the siloxane host matrices”, Materials, 2022, 15, 267, doi.org/ 10.3390/ma15010267.
2. Raduly, F.M.; Raditoiu, V.; Raditoiu, A.; Purcar, V. “Curcumin: Modern Applications for a Versatile Additive”, Coatings, 2021, 11, 519, doi.org/10.3390/coatings11050519.
3. Avram, S.; Stan, M.; Udrea A.M.; Buiu, C.; Boboc, A.A.; Mernea, M. “3D-ALMOND-QSAR Models to Predict the Antidepressant Effect of Some Natural Compounds”. Pharmaceutics, 2021, 13.9, 1449, doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091449.
4. Niculae, R.; Mernea, M.; Ghica, L.; Mihăilescu, D. F. ”A Computational Study on Ca2+ Modulation of ASIC 1 Pharmacologic Properties”. Studia Universitatis Babes-Bolyai, Chemia, 2021, 66(3).
5. Udrea, A. M.; Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, G.; Boboc, A. A.; Mares, C.; Dinache, A.; Mernea, M.; Avram, S. “Advanced Bioinformatics Tools in the Pharmacokinetic Profiles of Natural and Synthetic Compounds with Anti-Diabetic Activity”. Biomolecules, 2021, 11(11), 1692, doi.org/10.3390/biom11111692.
6. Raduly, F.M.; Rădiţoiu, V.; Rădiţoiu, A.; Purcar, V.; Ispas, G.; Frone, A.N.; Gabor, R.A.; Nicolae, C.-A. Optical Behavior of Curcuminoid
Hybrid Systems as Coatings Deposited on Polyester Fibers. Coatings 2022, 12, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020271.
7. Ispas, C.G.; Raduly, F.M.; Raditoiu, V.; Stan, R.; Raditoiu, A.; Purcar, V. “Extraction and characterization of bioactive compounds from ginger (Zingiber officinale)”, U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series B, 84, 2, 2022, 129-140.
8.Raduly, F.M.; Rădițoiu, V.; Fierăscu, R.C.; Rădițoiu, A.; Nicolae, C.A.; Purcar, V. Influence of Organic-Modified Inorganic Matrices on the Optical
Properties of Palygorskite–Curcumin-Type Hybrid Materials. Crystals 2022, 12, 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12071005.
9. Raduly, F.M.; Fierăscu, R.C. Hybrid Organic-Inorganic Materials Used to Improve the Environment and Human Health. Crystals 2022, 12, 1273.
doi.org/10.3390/cryst12091273 (editorial).
10. Mernea, M.; Ulăreanu, R.Ș.; Cucu, D.; Al-Saedi, J.H.; Pop, C.-E.; Fendrihan, S.; Anghelescu, G.D.C.; Mihăilescu, D.F. Epithelial Sodium Channel Inhibition
by Amiloride Addressed with THz Spectroscopy and Molecular Modeling. Molecules 2022, 27, 3271. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103271.
11. Al-Shammari, R. S. S.; Jaberi,A. K. H.; Lungu, A.; Brebenel, I.; Al-Sudani, W. K. K.; Al-Saedi, J. H. M.; Pop, C. E.; Mernea, M.; Stoian, G.; Mihailescu, D. F.
The antifungal activity of zein nanoparticles loaded with transition metal ions. Rev. Roum. Chim., 2021, 66(10-11), 819-828, DOI:
10.33224/rrch.2021.66.10-11.05.
Communications
1. Ispas, C.G.; Raduly, F.M.; Raditoiu, V.; Raditoiu, A.; Purcar, V. Extraction by ultrasounds and characterization of bioactive compounds from Zingiber
Officinale, Simpozionul international „Priorities of chemistry for a sustainable development-PRIOCHEM”. XVII th Edition, October 27 – 29, 2021,
Bucuresti, ROMANIA.
2. Ispas, C.G.; Raduly, F.M.; Raditoiu, V.; Stan, R.; Raditoiu, A.; Purcar, V. Textile Coatings Based on Ginger Extracts with Antimicrobial Activity, Virtual
International Scientific Conference on “Applications of Chemistry in Nanosciences and Biomaterials Engineering – NanoBioMat 2021”, 25-27 November
2021, Bucuresti, ROMANIA.
3. M. Raduly, V. Raditoiu, A. Raditoiu, V. Purcar, G. Ispas, Curcumin derived pyrazoles with potential antitumor activities, European Symposium on
Organic Chemistry-ESOC, Virtual mini symposium, 2021.
4. M. Stan, I. C. Nica, C. D. Nițu, M. Raduly, A. Dinischiotu, A. Speranta, D. Mihailescu, M. Mernea, In vitro study of curcumin derivatives with potential antitumor activity, 1st International Electronic Conference on Biomedicine, 2021.
5. M. Raduly, V. Raditoiu, A. Raditoiu, L. Wagner, V. Purcar, G. Ispas, R. Manea, C. A. Nicolae, Synthesis of asymmetric β-diketone derivatives and their complexation with lanthanides, 23rd JCF Frühjahrssymposium-online, 2021.
6. M. Raduly, V. Raditoiu, A. Raditoiu, V. Purcar, G. Ispas, R. Manea, A. Frone, M.L. Jecu, M. Călin, C. A. Nicolae, Curcumin derivatives immobilized in silica
matrices by sol-gel processes used as bioactive coatings, International Congress of „Apollonia” University from Iași, Romania, 2021.
7. Nica, I. C.; Mernea, M.; Stoian, Gh.; Dinischiotu, A. Natural aspirin-like compounds from white willow (Salix alba) bark extract prevent structural changes of human hemoglobin during in vitro non-enzymatic glycation and fructation, preserving its peroxidase and esterase activity, Med. Sci. Forum 2021, 2(1), 23; doi.org/10.3390/CAHD2020-08602.
8. Avram, S., et al. The study of natural compounds as antidepressants by bioinformatics methods, Presented at the 1st International Electronic Conference on Biomedicine. Vol. 1. 2021, https://doi.org/10.3390/ECB2021-10268.
9. Nitu, D. C., et al. Evaluating the ability of some curcumin derivatives to induce oxidative stress in cervix cancer, Presented at the 4th International European Conference on Interdisciplinary Scientific Research, 8-9 august 2021, Warsaw, Poland.
10. M. Stan, I. C. Nica, M. Raduly, M. Mernea, Evaluation of protective effect of some curcumin derivatives against gamma radiations, Al XIV-lea Congres
Național de Citometrie, 24-26 noiembrie 2021.
11. M. Raduly, V. Raditoiu, A. Raditoiu, V. Purcar, I. Raut, M. Constantin, C. Nicolae, R. Fierascu, Hybrid materials with antibacterial properties obtained
by deposition 1- dehydro-[6]-shogaol on modified palygorskite, International Congress of „Apollonia” University from Iași, Romania, 2022.
12. M. Raduly, V. Raditoiu, A. Raditoiu, V. Purcar, M. S. Stan, M. Mernea, C. Nițu, Synthesis of 2-phenyl-3,5-bis (styryl) pyrazole, curcumin derivațives
with potential antitumor properties, Romanian International Conference on Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, RICCCE 22, Sinaia, Romania, 2022.
13. V. Popa, S. Avramescu, M. S. Stan. Efectul antitumoral al extractului de coacăze negre asupra celulelor HeLa. The 15th national congress of
cytometry, 15-17 iunie 2022, Bucuresti, Romania (prezentare orală).
14. M. S. Stan, I. C. Nica, C. D. Nițu, M. Raduly, A. Dinischiotu, S. Avram, D. Mihailescu, M. Mernea. The potential of curcumin derivațives to induce
autophagy in cervix cancer cells. FEBS Advanced 2022 Lecture Courese 360o Lysosome: from structure to genomics, from function to disease-
Update. 4-9 Octombrie 2022, Kusadasi, Turcia (prezentare orală).
15. A. Vilaia, M. Mernea, D. F. Mihailescu, S. Avram, Molecular docking of two curcumin derivațives at beta-secretase and amyloid fibrils, 17th National
Conference of Biophysics with International Participation (CNB2022), 23-25 septembrie 2022, Târgu Mureş, România.
16. M. Mernea, M. E. Satmaru, A. N. Toma, C. D. Niţu, D. F. Mihăilescu, S. Avram, M. S. Stan, A molecular docking study on natural compounds as
anxiolytics and antidepressants, id sciforum-066187, acceptat pentru 8th International Electronic Conference on Medicinal Chemistry, 1-30 noiembrie
2022.
Cereri de brevet :
1. M. Raduly, V. Raditoiu, A. Raditoiu, V. Purcar, M. Bivolaru, I. Raut, M. Constantin, „Procedeu de funcţionalizare a fibrelor textile naturale celulozice cu
compoziţii antimicrobiene cu nanoparticule de seleniu”, Cerere de brevet nr. A 2022-00645/18.10.2022.
2. M. Mernea, M. Stan, C. Nica, C. Nitu, C. A. Matanie, S. Avram, Gh. Stoian „Procedeu de sinteza a unor nanoparticule de zeină încărcate cu extract de
ghimbir care prezintă potenţial terapeutic antitumoral”, Cerere de brevet nr A100628/13.10.2022.
Other scientific events:
International Exhibition of Inventions – INVENTICA 2021, June 23-25, Iasi, Romania.

Contact
National Institute for Research & Development in Chemistry and Petrochemistry – ICECHIM
202 Splaiul Independentei, 6th District, 060021 Bucharest, Romania
Project manager: Florentina Monica Raduly
Phone: +40 21 316.30.62/118
Fax: +40 21 312.34.93
E-mail:
Web: www.icechim.ro
